
Constant Coughing - Could be Bronchitis
What is Bronchitis?
Bronchitis is a respiratory condition characterised by inflammation of the bronchial tubes, which are the passages that carry air to and from the lungs. This inflammation leads to a persistent cough and production of mucus, making it difficult for individuals to breathe comfortably. Bronchitis can be classified into two main types:
● Acute Bronchitis: Acute bronchitis is typically caused by a viral infection such as the common cold or flu and usually resolves on its own within a few weeks.
● Chronic bronchitis Chronic bronchitis is characterised by a persistent cough with mucus for most days of the month, lasting for at least three months a year, and recurring for at least two consecutive years. If you have chronic bronchitis, you may also have Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). It is a long-term condition that requires ongoing management.
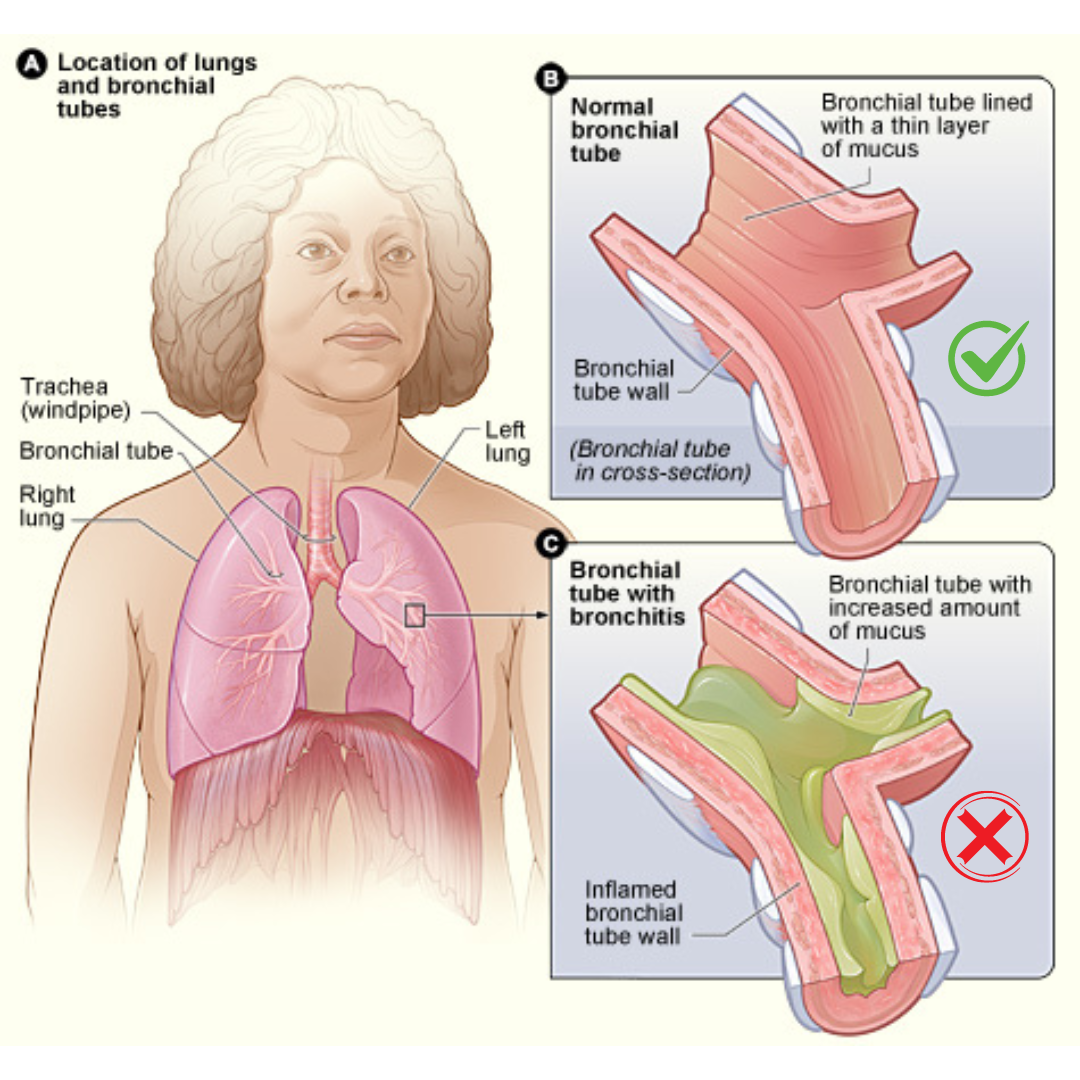
Reasons for getting the Bronchitis disease:
Bronchitis can occur due to several reasons including:
- Viral infections: The most common cause is a viral infection, such as the flu or a cold.
- Bacterial infections:Less commonly, but it can be caused by a bacterial infection.
- Smoking: Tobacco smoke is a significant risk factor, as it irritates the bronchial tubes and can lead to chronic bronchitis.
- Air pollution: Exposure to polluted air, dust, fumes, and chemicals can also trigger bronchitis.
- Allergens: Exposure to allergens like pollen, mould, or pet dander can contribute to bronchitis.
- Weakened immune system: Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as the elderly, infants, or those with chronic illnesses are more susceptible.
What are the Symptoms of Bronchitis:
The symptoms of bronchitis can vary depending on the type of it and the primary symptom of bronchitis is a persistent cough that often produces yellow-green mucus. Other symptoms can have:
- Shortness of breath or wheezing
- Frequent respiratory infections
- Mild fever, Headache, Fatigue
- Tightness in the chest
- Sore throat and Runny or blocked nose
Complications of untreated Bronchitis
If bronchitis is not treated appropriately, it can lead to several complications:
- Pneumonia: An infection of the lungs that can occur when bacteria infect the airways and lungs, especially in individuals with weakened immune systems.
- Worsening of chronic conditions: Individuals with asthma or COPD may experience exacerbated symptoms and increased frequency of attacks.
- Respiratory failure: In severe cases of chronic bronchitis, the lungs may become unable to provide enough oxygen to the body, leading to respiratory failure, which is a medical emergency.
Diagnosis of Bronchitis:
Diagnosing bronchitis typically involves the following steps:
- Medical History: The healthcare provider will ask about your symptoms, duration, and any potential exposure to irritants or infections.
- Physical Examination: A thorough examination, including listening to the lungs with a stethoscope to detect wheezing or abnormal sounds.
-
Diagnostic Tests:
- Chest- X-ray to rule out pneumonia or other lung conditions and assess the extent of lung damage.
- Pulmonary function tests to assess lung capacity and airflow, particularly in chronic bronchitis.
- Sputum test for analysing mucus from the lungs to identify any bacterial infections.
- Blood tests to look for infections or check overall health.
Treatment of Bronchitis:
Treatment approaches depend on the types of bronchitis:
Acute Bronchitis: Acute bronchitis often resolves on its own within a few weeks. Treatments primarily focus on relieving symptoms:
- Hydration, rest and reduce pain with over-the-counter medications.
- Humidification: Utilise a humidifier or take a hot shower to help loosen mucus.
- Cough Medicines can help loosen mucus.
Chronic Bronchitis: Treatment for chronic bronchitis is aimed at managing symptoms and improving quality of life:
- Medications:
- Antibiotics if bacterial infection is present.
- Anti-inflammatories to reduce inflammation.
- Bronchodilators to open airways and ease breathing.
- Mucus-clearing devices: These devices assist in coughing up mucus more effectively if required.
- Pulmonary rehabilitation: A program that includes exercise, education, and support to help manage chronic lung conditions.
- Oxygen therapy: For individuals with severe chronic bronchitis, supplemental oxygen may be necessary to maintain adequate oxygen levels.
Prevention of Bronchitis:
Preventing bronchitis involves several proactive measures:

Taking preventive steps and getting timely medical care can lower the risk of bronchitis and its complications. If you suspect you have bronchitis or are experiencing persistent respiratory symptoms, consult a doctor for proper evaluation and treatment.
 Back
Back