
A cardiac arrest is an electrical problem triggered by a sudden disruption of the heart's rhythm. It is when the heart suddenly or unexpectedly stops beating due to an irregular heart rhythm. As a result, blood does not properly circulate in the body and there is a stop of blood flow to the brain and other organs.
Cardiac arrest happens in many cases without warning. This is why people also call it sudden cardiac arrest. It is a serious medical emergency and a life-threatening condition that can become fatal if you do not get immediate medical attention.

Cardiac arrest happens suddenly, often without any prior symptoms. However, some people may experience the early warning signs.
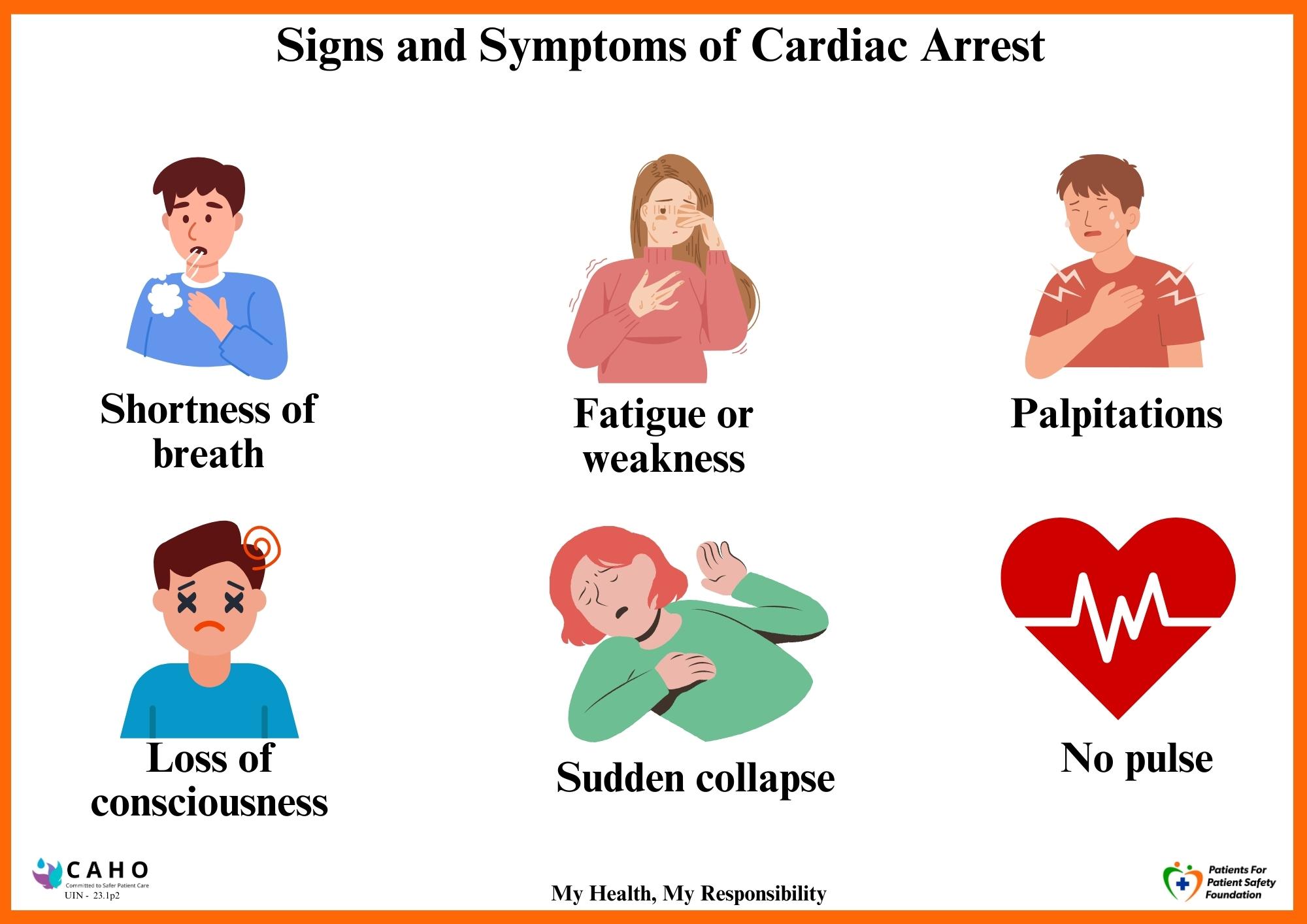
The most critical symptoms are the sudden loss of consciousness, lack of pulse, and absence of normal breathing, which indicate the heart has stopped pumping blood effectively.
Cardiac arrest is caused by a malfunction in the heart's electrical signals, leading to abnormal heart rhythms called arrhythmias. The most common cause is ventricular fibrillation, where the heart's lower chambers (ventricles) quiver instead of pumping blood effectively.
The most common causes are:
Time is critical in a cardiac arrest situation.
Remember, prompt CPR can significantly increase your chances of survival.
Cardiac arrest can lead to death if there is no treatment within minutes, it encompasses a range of serious challenges, including brain damage, organ dysfunction, physical disabilities, emotional trauma, reduced quality of life, and mortality.
Tests for sudden cardiac arrest often include:
Cardiac arrest treatment has to start immediately, regardless of where it has occurred. Survival can be as high as 90% if treatment starts within the first minutes after sudden cardiac arrest. The rate drops by about 10% each minute longer.
By incorporating these preventive measures into daily life, individuals can reduce their risk of cardiac arrest and improve overall heart health. Additionally, it is essential to be aware of the signs and symptoms of cardiac arrest and seek immediate medical attention if they occur. Early intervention can significantly improve the chances of survival and recovery from cardiac arrest.