Heart Attack - Symptoms, Causes, Treatment, and Prevention
Introduction:
A heart attack is a serious medical emergency, in which the supply of blood to the heart is suddenly
and severely reduced or cut off, this interruption in blood flow can cause damage to the heart muscles
and, if left untreated, can lead to severe complications or even death.
Heart attacks can be life-threatening, but being aware of the warning signs and acting fast can make a
significant difference. If you recognize the symptoms of a heart attack and seek immediate medical
attention, you not only increase your chances of survival but also improve your prospects for a full
recovery and a healthy lifestyle.
Symptoms of a Heart Attack:
You may have early symptoms like breathlessness while walking or climbing stairs or chest discomfort.
Common symptoms include:
- Chest pain: A feeling of pressure, heaviness, tightness or squeezing across your
chest. The chest pain can be severe. Some people experience minor pain and confuse it with
indigestion.
- Shortness of breath. This can occur with or without chest discomfort.
- Pain in other parts of the body which feels as if the pain is spreading from
your chest to your arms (usually the left arm). Also pain in jaw, neck, back, and tummy.
- Heavy sweating
- Feeling of anxiety (similar to a panic attack)
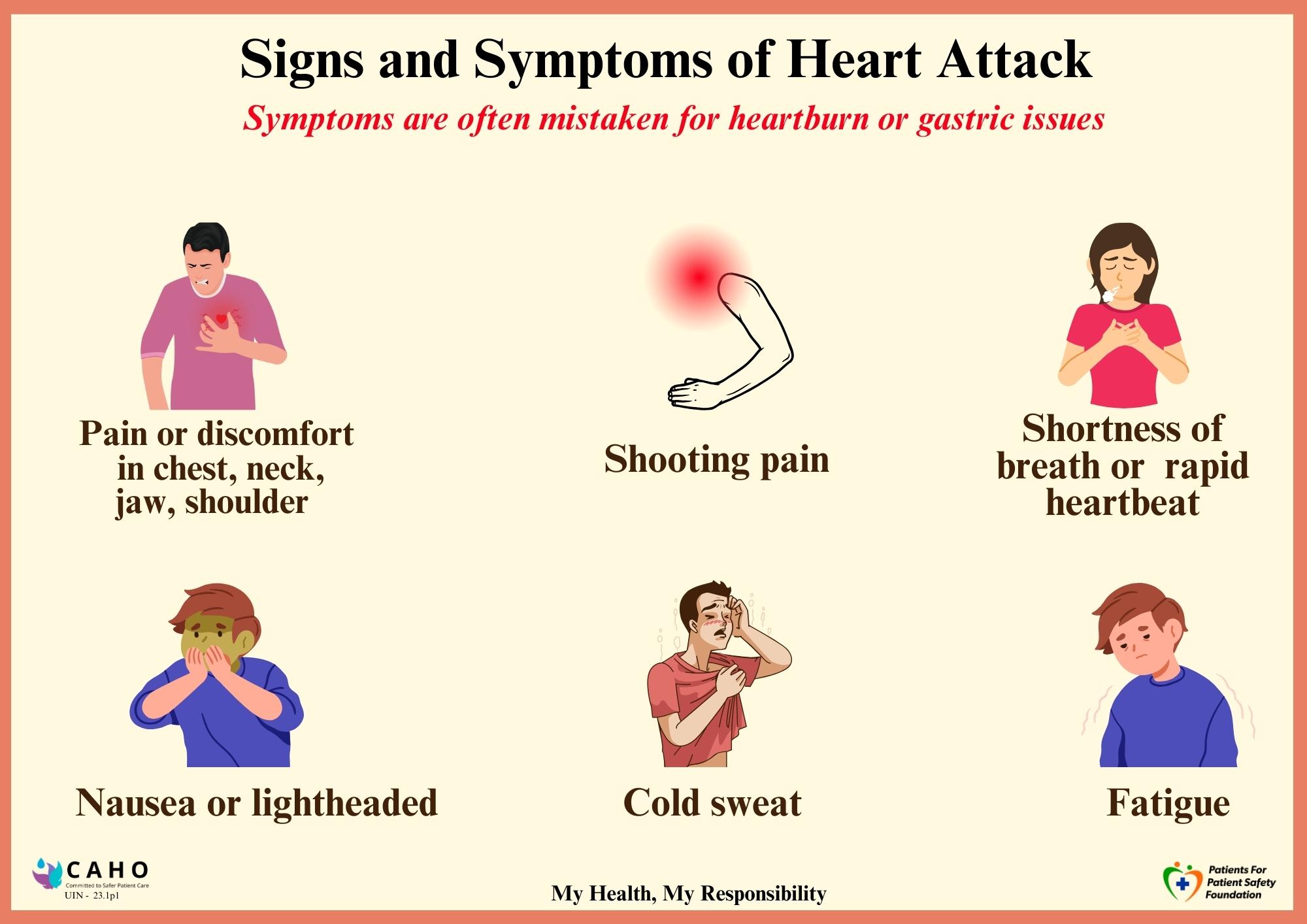
Other signs include nausea or lightheadedness. Often a heart issue is mistaken as heartburn or
gastric issues and delay could lead to serious consequences and delayed treatment.
Who is at risk:
A heart attack can happen to anyone, however, certain factors can increase your risk. You may be at a
higher risk for a heart attack if you
- Have diabetes and suffer from high blood pressure or high cholesterol.
- Are obese or overweight.
- Smoke or are exposed to secondhand smoke.
- Experience significant stress on a regular basis.
- No physical activity.
- Have a family history of heart disease.
What to do if you feel you are having a Heart Attack:
- Inform someone nearby immediately
- Open the front door if alone
- Rest and try to stay as calm as possible. Stress and panic can worsen the
situation.
- Chew aspirin if you are not allergic to it and your doctor has not advised
against its use.
- Call your doctor, share your symptoms, and take advice.
- Do not drive yourself. Ask for a Cardiac Ambulance. Dial 102, If delayed, have a
neighbour or a friend drive you to the nearest hospital.
Guide on how to help someone experiencing a Heart Attack:
- Stay calm: Try to keep the person calm. Stress can worsen the situation. Help the
person sit down and make them as comfortable as possible.
- Call a physician for advice.
- If the person is not allergic to aspirin, have them chew one regular strength.
- Perform CPR : If the person becomes unresponsive and stops breathing,
you may need to perform CPR if you are trained to do so.
- Call for Cardiac Ambulance 102. If delayed, drive the patient to the hospital
What are the possible complications of a Heart Attack:
- Damage to the heart or heart valves
- Abnormal heart rhythms
- Another heart attack
- Heart failure because the heart doesn't pump as well as it once did
- Shock and other organ failure
- Death
How is Heart Attack diagnosed:
Diagnosing a heart attack often happens in an emergency department. There, a healthcare provider will
ask you about your health history and do a physical exam. You may also need some tests, such as:
- Imaging test
- Electrocardiography (ECG)
- Blood tests
- Echocardiography (Sonography)
How is a Heart Attack treated:
The main goals of heart attack treatment are to restore blood flow to the affected heart muscle as
soon as possible and minimize damage to the heart. Treatment typically involves:
- Medications like aspirin to stop blood clotting Other medicines are also given during or after a
heart attack to help the heart work.
- Surgical and other procedures may be done in rare case to open a blocked artery.
Prompt treatment and lifestyle changes are crucial for minimizing heart damage and preventing
complications after a heart attack.
Preventive Measures:
- Engaging in regular physical activity.
- Adopting a heart-healthy diet.
- Managing stress.
- Quitting smoking and alcohol intake.
- Taking prescribed medications.
- Regular heart health check up.
By adopting these healthy habits and managing risk factors, you can reduce your chances of having a
heart attack and improve your overall cardiovascular health.


